Peering Beneath the Surface: Ground Penetrating Radar Investigations Explained
Ground Penetrating Radar, or GPR, is recognized as a innovative instrument for non-invasive subsurface exploration. Such advanced method enables professionals from various fields to look below ground level and gather critical information about what lies below, without the need for digging. Understanding the components of a GPR survey and its significance is vital for engineers, construction supervisors, archaeologists, and environmental specialists alike. Through the use of this technology, these industries can significantly enhance their project outcomes, ensuring safety and efficiency while minimizing expenses.
In this piece, we will explore the numerous benefits of GPR surveys, from their function in construction and engineering projects to their applications in archaeology and environmental studies. We'll investigate the technology behind GPR, contrasting it to conventional surveying techniques, and address common myths surrounding its use. Additionally, this comprehensive guide will offer insights into how to choose the right GPR survey service, the cost considerations involved, and how GPR surveys are revolutionizing infrastructure inspections today. Whether you're a beginner or seeking to improve your understanding, this guide will provide you with a deeper understanding of GPR surveys and their critical role in contemporary industry.
Grasping GPR Investigations along with Their Value
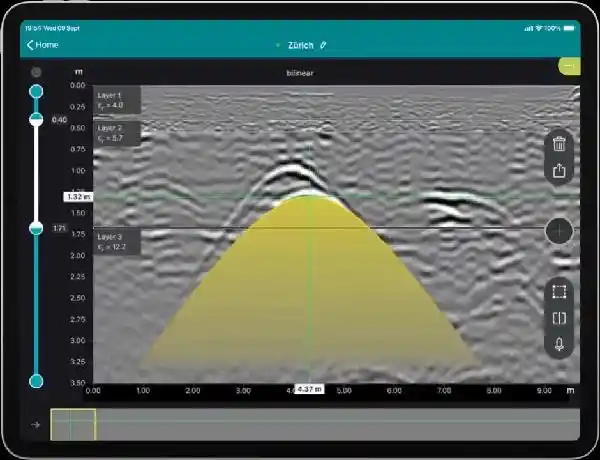
Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR) studies constitute non-invasive geophysical procedures used to examine what lies beneath the surface. Using sending rapid frequency electromagnetic waves within the earth and measuring the echoes, GPR can discover plus chart different underground features, like infrastructure, voids, and geological formations. This method is essential for various fields, like infrastructure development, archaeology, environmental assessment, and civil engineering, because it supplies important insights without requiring significant ground disturbance.
The importance of GPR studies stems from their capacity to enhance security plus effectiveness in different endeavors. For building https://yogaasanas.science/wiki/Navigating_the_Hidden_A_Journey_into_GPR as engineering projects, identifying underground utilities and possible risks prior to commencing work can prevent incidents and costly disruptions. In archaeological efforts, GPR helps reveal artifacts along with structures buried under the soil without disrupting the area, allowing for a more respectful as well as in-depth exploration of archaeological locations.
Furthermore, GPR methods continues to be constantly advancing, leading to it being ever more precise along with attainable. With more fields realize the benefits of conducting GPR studies, GPR's function for environmental assessments and geotechnical investigations is increasingly essential. By providing comprehensive information into subsurface conditions, GPR aids decision-making in strategic decisions, which can result in better project outcomes together with reduced ecological footprint.
Benefits and Applications of GPR Surveys
GPR surveys offer numerous advantages, making them an essential tool for different industries. One of the main benefits is their ability to provide non-destructive subsurface imaging, enabling for the detection of buried structures such as conduits, cables, and geological formations without disturbing the ground. This leads to less hazardous and more efficient project execution, minimizing the risks connected to accidental utility strikes and cutting the costs of remediation. Moreover, GPR technology is comparatively quick, facilitating rapid data collection and analysis, which is crucial in time-critical projects.
The applications of GPR surveys extend across a wide range of fields. In building and engineering, GPR is frequently used to assess site conditions before excavation, guaranteeing compliance with local laws and guidelines. This technology is also extremely valuable in environmental assessments, where it helps identify pollutants and stratigraphic layers. Additionally, GPR is applied in archaeological investigations to uncover buried artifacts and structures while preserving the integrity of the site, thus minimizing disturbance to cultural heritage.
Another major application of GPR surveys is in the realm of construction inspection and maintenance. Engineers use GPR to assess the condition of concrete structures, detecting delamination or voids that may compromise safety. This preventive approach to infrastructure management prolongs the lifespan of assets and enhances safety for the public. Overall, the versatility and precision of GPR surveys make them an crucial resource across different sectors, demonstrating their critical role in modern engineering practices.
Ground Penetrating Radar Surveys: Technology, Accuracy, and Future Developments
GPR technology employs high-frequency electromagnetic waves to detect and map underground structures. The system includes a signal generator that emits radar pulses into the ground and a sensory unit that receives the returned signals. This process produces images that show the variations in material and the presence of items like pipes, voids, or archaeological artifacts. As technology progressed, GPR systems have become more compact, user-friendly, and able to generating better quality images, making them vital tools in different industries.
Precision is a critical concern in GPR surveys, as it directly influences the trustworthiness of the data collected. Various factors can influence the accuracy of GPR results, including soil structure, water content, and the depth of the target. Modern GPR systems are integrated with advanced processing algorithms that improve signal interpretation, leading to better accuracy in identifying underground infrastructure and structural irregularities. Continuous advancements in software and data analysis techniques are predicted to further boost the reliability of GPR surveys in exactly representing subsurface conditions.
As we look forward, the future of GPR technology is encouraging. With the integration of artificial intelligence and data-driven learning, processing speeds and accuracy levels are expected to improve. website link will enable more efficient interpretation of detailed data sets, leading to more rapid decision-making in building and environmental assessments. The growing emphasis on infrastructure resilience and sustainability will drive demand for GPR applications in analyzing and maintaining structural integrity, ensuring that GPR stays at the forefront of modern surveying techniques.